Into the Darkness:
An Uncensored Report from
Inside the Third Reich at War
by Lothrop Stoddard
Chapter 5: This Detested War
The Germans detest this war. That was the ever deepening impression I got throughout my stay in the Third Reich. Wherever I went, it was the same story. Public opinion in Berlin about the war tallied with what I found in my travels through West Central Germany as far as the Rhineland and the North Sea Coast, and through South Germany to Vienna. This attitude is shared by Nazis and non Nazis. On this point there is no difference between them.
Yet we should clearly understand the reason for this agreement. It is not founded on moral opposition to war as such. In the Third Reich, pacifism is akin to treason. Such genuine pacifists as may still exist there outside of concentration camps are so carefully camouflaged that, like Arctic hares in winter, they cannot be detected against the landscape.
German aversion to the present war, therefore, though general and genuine, is due to strictly practical reasons. What maddens the Germans is that they are obliged to fight desperately in order to keep what they now hold. During the past three years they have marched with giant strides toward the realization of one of their oldest dreams the domination of Central Europe. Long before Hitler was even heard of, MittelEuropa was a phrase to conjure with. Rightly or wrongly, most Germans believe that hegemony over mid-Europe is necessary for their national future. As often happens in such cases, they have “rationalized” their desire until they have come to think it their just due. So whatever is done to achieve this goal seems to Germans quite right and proper.
Regions of Europe (click to enlarge)
Embattled Poland was the last local obstacle to MittelEuropa. By a series of amazing diplomatic victories, Adolf Hitler had taken all the other hurdles without firing a shot. This led the average German to believe that the Fuehrer would complete the process without recourse to arms. Like Al Smith, he said: “Look at the record!” In German eyes, the Anglo French guarantee to Poland was wholly uncalled for. Why, they asked, should Britain and France stick their noses into what was none of their business? Most Germans did not believe that the Western Powers would risk a general war over Poland. The German people was thus psychologically unprepared for what actually happened.
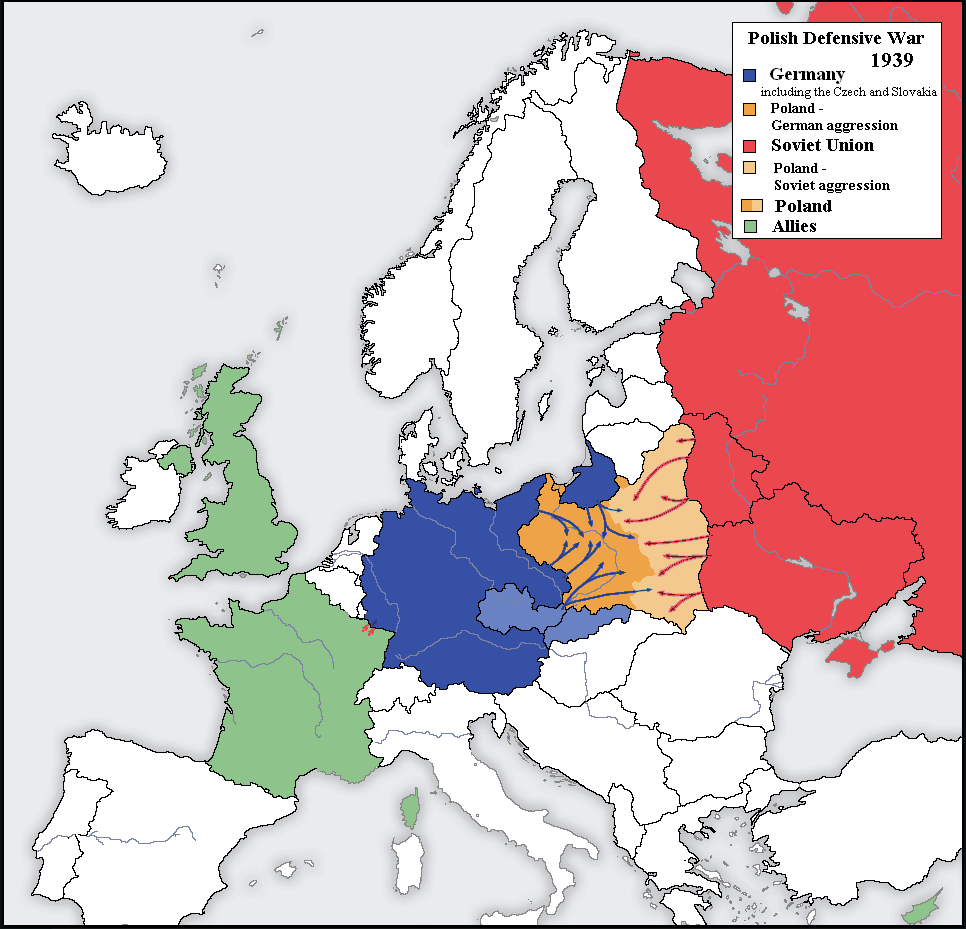
German and Soviet attack on Poland 1939 (click to enlarge)
When they found themselves suddenly plunged into a decisive struggle with the Western Powers, Germans were torn between two emotions: disgust at what they considered a stupidly needless war, and fear for the consequences which it might involve. All sorts of persons I talked with stigmatized the war as a tragic blunder. Some of them went so far as to criticize their Government for having acted too precipitately. They thought the war could have been avoided by cleverer diplomacy. But those very persons approved of the end sought, no matter how sharply they disapproved of the means. Even ardent Nazis, who claimed that Hitler had taken the only possible course and who professed perfect confidence in ultimate victory, revealed the same underlying mood of regretful irritation.
“Think of it,” they would explain, “here we were busy making over our country, and now we have to lay aside most of our fine reconstruction plans to go and fight it out with those damned Englishmen!”
In this respect, Germany’s attitude can perhaps best be compared to that of the big winner in a poker game who was just raking in the chips when somebody kicked over the table.
Yet, needless or not, the great war was here! That was the grim reality which suddenly confronted the German people. And they seem to have been literally stunned. At first they just couldn’t believe it was true. From all I could gather, their attitude during the first month or so was that of a man in a nightmare who tries to wake up and find it is only a bad dream. The amazingly quick military decision in Poland produced, not so much popular jubilation over the victories themselves, but rather a belief that Poland’s rapid collapse would cause Britain and France to accept the situation, and that the war in the West would therefore soon be over.
That was the prevailing mood when I entered Germany toward the end of October, 1939. Almost everyone I talked to, from hotel waiters and chambermaids to chance acquaintances in restaurants and cafes, asked me if I didn’t think the war would end soon. And they didn’t need any tactful prodding. They usually raised the question themselves early in the conversation.
Another irksome feature in German eyes was that, as time passed and nothing much happened in a military way, the war tended to become a bore. No one could get very excited over intermittent land skirmishes, a few airplane dogfights, or an occasional submarine exploit. Meanwhile the numberless irritations of a strictly rationed life went steadily on. People in the cities hadn’t any too much to eat, and they had to fuss with their multitudinous food cards every time they bought a meal or went marketing. They certainly had none too much to wear, yet to get that little they must go through the rigamarole of clothing cards and Bezugscheine. Practically everything could be bought only in limited amounts, and many things could not be bought at all. Social life had been disrupted or distorted by the general blackout. While as yet there was little acute suffering, everyday life was full of minor irritants and nothing was quite normal.
The result of all this was a depressing mental atmosphere. People were obviously uneasy, dully unhappy, and uncertain about the future. At first I thought this indicated really bad morale and I began to wonder whether the German people might not soon crack under the strain.
Presently, however, I revised my opinion. For one thing, I recalled from past experience that Germans have always been complainers. They seem to enjoy having what the English call a “grouse” with Berliners perhaps the biggest grousers of the lot. The Germans have a slang word for this sort of thing. They call it meckering, which means the ill-natured bleating of a billy goat. Indeed, a long-term American resident of Berlin told me that he considered meckering a healthy sign; it is when the German says nothing that you must look out for trouble.
Another thing I noted was that, with every passing week, the Germans were putting aside their wishful thinking for a quick peace and were mentally accepting the stern reality that they were in for what would probably be a long and bitter struggle. Despite surface appearances, therefore, it became clear to me that the German people was not in what the French call a “defeatist” mood. Not once did I hear a single German, high or low, rich or poor, suggest even in the most confidential talk that the Reich should throw up the sponge and accept peace terms in accordance with British and French war aims. To give up Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Austria, for example, seems to most Germans quite impossible. By gaining control over those lands, the Germans believe they have got what they have long wanted an unshakable economic and political supremacy in Central Europe. Since Britain and France challenge that supremacy and seek to overthrow it, the attack must be met and broken, no matter how long the job may last or how painful it may become. That, in a nutshell, was the basic popular mood which I saw ripen and harden under my eyes.
England was regarded as the archenemy. There seemed to be almost no hostility towards the French, who were looked upon as Britain’s cat’s-paws and dupes. Popular hostility toward Britain, however, grew visibly more intense from day to day. In part, this was undoubtedly due to the violent diatribes in the press and in public utterances of official spokesmen; in part it was a natural and inevitable reaction against the country which was held responsible for all the discomforts of the wartime present and the dangers of the future. But, during my stay in Germany, this anti British trend seemed to be a dour anger rather than flaming emotion. People did not go around shouting Gott strafe England! as was done in the last war; neither was anything written similar to Lissauer’s Hymn of Hate. Popular hysteria was notably absent.
Indeed, the whole war psychology of the German people today seems to be quite different from that of a quarter century ago. Kaiser Wilhelm loved military glitter and trappings; his army was the Empire’s Exhibit A, and writers like Bernhardi glorified war as a healthful exercise to keep a people fit or even as a “biological necessity.” So, when real war came in 1914, the Germans went into it with jubilation. And, for the first year or two, they kept up this hysterically romantic mood.
You find nothing like that spirit in Germany today. Bitter memories of the last war and the chronic misfortunes which ensued have cured the present generation of the war heroics in which their fathers so liberally indulged. To be sure, the average German seems ready to fight and die for what he believes to be his rightful place in the world. However, he doesn’t sentimentalize over it. He’s usually hard-boiled on the subject. It’s just a dirty chore that, if needs be, must be done.
That seemed to suit the Nazi Government, which made no attempt to whip up popular emotion by either military or Party displays. During all the months I was in Berlin or other cities, I never saw any of those big parades with blaring bands and dress uniforms which we are apt to associate with wartime. The only marching soldiers I saw were occasional platoons of infantry going to change guard where sentries were posted. And the German soldier, in his lead colored steel helmet, his slate green clothes, and his clumping high boots, is a severely practical person. I should think it would be hard for the most sentimental Teuton to work up much of a thrill over this matter of fact fighting man.
Another noteworthy point is that the Government made no attempt to ease the people into the war by tactful stages. Quite the reverse. Nazi spokesmen tell you frankly that they cracked down hard from the start and made things just about as tough as the civilian population could bear. Indeed, they say that severe rationing of food and clothing from the very beginning was done not merely to avert present waste and ensure future supplies; it was done also to make people realize that they were in a life and death struggle for which no sacrifice was too great.
This was stiff medicine for a people as stunned, depressed, and jittery as the Germans certainly were during the first two months of the war. I do not recall any other Government which has prescribed a course of treatment so drastic, under similar circumstances. Flag waving and assorted heroics are the orthodox formula.
Paul Joseph Goebbels – Reich Propaganda Minister
I was therefore deeply interested to discuss this original method with the man who carried it out. He was no less a person than Dr. Paul Joseph Goebbels, head of the vast propaganda machine which is perhaps the most outstanding feature of the Third Reich.
This lithe, brunet Rhinelander, with his agile mind, cynical humor, and telling gestures, is an excellent person to interview. He is mentally on his toes every instant, and he is full of what the journalist calls “good lines.” He got one of them off early in our conversation when he stigmatized the British blockade of Germany by exclaiming:
“It’s high time that forty million people stopped dictating to eighty million when they should have a cup of coffee!”
As Dr. Goebbels warmed to his subject, his words flowed with the smoothness of a well oiled machine.
“Mr. Minister,” I began, broaching the subject uppermost in my mind, “the thing that strikes me most since I’ve been in Germany this time is the great difference between the popular mood now and in the last war. No hurrahs, parades, bands, and flowers like in 1914.”
“That’s right,” he shot back quickly, “and the reason is very simple. In 1914 the German people didn’t know what it was all about. They had no clear war aim. Some French iron mines! A bit of Belgium! Gott strafe England! Slogans and phrases! That’s no way to wage a war. And our rulers then couldn’t make them understand. They were an aristocratic caste, out of touch with the people.”
“And now?” I put in.
“Now?” he countered. “We National Socialists are men of the people. We know how our fellow citizens think and how to make them understand. But, really, the British have done it for us. They’ve given us our war aim by forcing the war on us.”
“Meaning what?” I asked.
“Meaning this,” he replied. “We made it clear to the British that we didn’t want to disturb their empire. We carefully kept our hands off sore spots like India and Ireland. Why, we even offered to give them a military guarantee of their empire’s integrity. But we made it clear that, in return, they were to keep their hands off our sphere of interest Central Europe. Well, they wouldn’t have it that way. They’re trying to crush us. So, this time, every German knows what it’s all about.”
“And that’s why they’re so quiet about it?” I asked.
“Exactly,” nodded Dr. Goebbels with a quick smile. “We Germans don’t like this war. We think it’s needless silly. But, since England feels that way, we see it’s got to be gone through with. The average German feels like a man with a chronic toothache the sooner it’s out, the better. And he doesn’t need brass bands and flowers to get it over with. That’s where our aristocrats went wrong last time. They forgot old Bismarck’s saying that hurrah patriotism isn’t like pickled herring that you can put up in barrels and store away for years. Listen! If I wanted to get the German people emotionally steamed up, I could do it in twenty four hours. But they don’t need it they don’t want it.”
“Then, psychologically ,” I began.
Georges Clemenceau – French Prime Minister ( Nov 16, 1917 to Jan 20, 1920)
Dr. Goebbels cut in with a sweeping gesture.
“Psychologically,” he answered, “we are way ahead. Last time, I admit, it was very different. Then, at the crucial moment, both France and England produced great men Clemenceau and Lloyd George, both men of the people. If we on our side could have produced a Bismarck or a Hitler, we should have won. This time, we have the right men and the others haven’t. We National Socialists understand profoundly that it is the human being who counts not just material resources. England is socially unsound. She is a colossus with feet of clay. Furthermore, England has a negative, defensive war aim. This time, it’s the British who talk in vague phrases like ‘aggression.’ What does it mean to Tommy in the trenches to tell him he’s fighting ‘aggressors’?”
“Would you mind enlarging on that a bit, Mr. Minister?” I asked.
David Lloyd Georges – British Prime Minister ( Dec 7, 1916 to Oct 22, 1922)
“Certainly not,” he answered. “The more you examine British war aims, the more negative they appear. The English admit they have nothing tangible to get out of this war but that they have a lot to lose. We, on the other hand, have very little to lose and a lot to win. Here we Germans are eighty million of us, all together. And right next to us is our sphere of influence in Central Europe everything under one roof. Sooner or later, we massed Germans are bound to get what we need. The British, on the contrary, are spread all over the map. They draw their resources from the four corners of the earth. Their empire is too dispersed, too artificial. They’re bound to lose in the long run.”
“Then the British Empire,” I began.
“Please understand,” broke in Dr. Goebbels. “We had no designs upon it. We showed this clearly when we made the naval treaty with England limiting our fleet to one third their size. In face of that fact, any responsible German who might have meditated an attack upon the British Empire would have been guilty of criminal madness. It is only now, when England forces us to a life and death struggle, that we hit back in every possible manner. All we asked was that England regard us, too, as a great nation with its own special sphere. After all, nations should be treated on their merits, for what they are. Live and let live was our motto toward England. It is the British who would not have it that way.”
“The English,” I remarked, “seem to believe that this is a struggle between democracy and dictatorship.”
“Dictatorship!” shot back Dr. Goebbels scornfully. “Isn’t the National Socialist Party essentially the German people? Aren’t its leaders men of the people? How silly to imagine that this can be what the English call dictatorship! What we today have in Germany is not a dictatorship but rather a political discipline forced upon us by the pressure of circumstances. However, since we have it, why shouldn’t we take advantage of the fact?”
“Just what do you mean by that, Mr. Minister?” I queried.
“I’ll give you an example,” answered Dr. Goebbels. “Take the difference between the way we and the English handle radio. We don’t let our people listen to foreign broadcasts; the English do. Why should we permit our people to be disturbed by foreign propaganda? Of course we broadcast in English, and the English people are legally permitted to listen in. I understand lots of them do. And can you imagine what is one of the chief discussions about it across the Channel? It is, whether our German announcer has an Oxford or a Cambridge accent! In my opinion, when a people in the midst of a life and death struggle indulge in such frivolous arguments, it doesn’t look well for them.”
“Then, Mr. Minister,” I asked, “you don’t think there is much likelihood that history will repeat itself?”
Dr. Goebbels’ dark eyes lighted.
“History never repeats itself,” he exclaimed with a sweeping gesture.
Goebbels in his office
“History is like a spiral and we believe that, since the last war, we have made an ascending turn while Britain has made a descending one. Today, we have a national unity, discipline, and leadership vastly superior to that of 1914, and even more superior to anything which England has as yet produced. The rightful claims of the German people were thwarted a generation ago. They cannot be denied a second time.”
So saying, the world famous Minister of Popular Enlightenment and Propaganda rose briskly from his chair and gave me a vigorous handshake. One last look at the slim, dynamic figure and his spacious office hung with historic portraits, and the interview was over. I had got “the dope,” all right, from headquarters. And the more one studies the text of that interview, the more revealing it becomes in many ways! It certainly was propaganda of the Goebbels brand.
———————————-
Book Reviews
Chapter 1: The Shadow
Chapter 2: Berlin Blackout
Chapter 3: Getting on with the Job
Chapter 4: Junketing Through Germany
Chapter 5: This Detested War
Chapter 6: Vienna and Bratislava
Chapter 7: Iron Rations
Chapter 8: A Berlin Lady Goes to Market
Chapter 9: The Battle of the Land
Chapter 10: The Labor Front
Chapter 11: The Army of the Spade
Chapter 12: Hitler Youth
Chapter 13: Women of the Third Reich
Chapter 14: Behind the WinterHelp
Chapter 15: Socialized Health
Chapter 16: In a Eugenics Court
Chapter 17: I See Hitler
Chapter 18: MidWinter Berlin
Chapter 19: Berlin to Budapest
Chapter 20: The Party
Chapter 21: The Totalitarian State
Chapter 22: Closed Doors
Chapter 23: Out of the Shadow
———————————-
Into the Darkness: Chapter 5 (PDF). >> Into the Darkness – Chapt 5 – This Detested War
Version History
Version 8: Apr 30, 2022. Re-uploaded images and PDF for katana17.com.
Version 7: Jun 17, 2015. Formatting changes.
Version 6: Nov 28, 2014. Added PDF file (Ver 2) of this post.
Version 5: Mon, Jun 9, 2014. Added PDF file of this chapter for download.
Version 4: Wed, Feb 5, 2014. Added Chapter links.
Version 3: Mon, Jan 27, 2014. Quoted text italicized.
Version 2: Some pics added.
Version 1: Published May 11 2013 – Text and some pics added.





Pingback: Into the Darkness : Chapter 3 – Getting on with the Job | katana17
Pingback: Into the Darkness : Chapter 1: The Shadow | katana17
Pingback: Into the Darkness : Chapter 6: Vienna and Bratislava | katana17
Pingback: Into the Darkness : Chapter 8: A Berlin Lady Goes to Market | katana17